The ESG information disclosure of building materials companies is becoming more and more standardized, and the proportion of ESG information disclosure continues to rise
Under the unified deployment of the China Securities Regulatory Commission, the Shanghai and Shenzhen North Stock Exchanges have recently solicited public opinions on the "Sustainability Reporting Guidelines" (hereinafter referred to as the "Guidelines", the "Guidelines" are also known as ESG reports), and listed companies that are required to disclose the "Sustainability Report" should publish the 2025 "Sustainability Report" before April 30, 2026.
According to industry insiders, the "Guidelines for Sustainable Development Information Disclosure" is intended to urge listed companies to better implement the new development concept while pursuing profits, and guide listed companies to more comprehensively reveal the results of improving sustainable development capabilities.
It is understood that in the future, China's three major exchanges will continue to enrich and improve the sustainable development rule system, product system and service system, and promote the formation of a high-quality green and sustainable development financial market ecology. So what about the disclosure of ESG reports in related industries?
The recently released "Research Report on ESG Development of China's Building Materials Industry" (hereinafter referred to as the "Report") found that the ESG information disclosure of building materials enterprises is becoming increasingly standardized, and the information disclosure has responded positively to the framework of international rating agencies and the SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations), and gradually enriched the content of the report.
In the past three years, the proportion of ESG reports released by the building materials industry has increased year by year
The quality of ESG information disclosure of cement, concrete and other enterprises is relatively high
According to the latest statistics, according to the classification standards of the domestic building materials industry, at present, there are about 130 enterprises in the building materials industry listed at home and abroad in China. Among the 125 companies selected in the report, there are 86 A-share listed companies, 4 A+H shares, 33 H-shares (Hong Kong H-shares), and 2 T-shares (Taiwan T-shares).
According to the statistics of Beijing Guojian Lianxin Certification Center Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Guojian Certification) and Miaotou Information Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as MioTech), as of May 2023, among the 125 listed building materials companies, the companies that have published ESG reports and social responsibility reports containing ESG information account for 45.6% of the total number of listed companies.
It should be noted that although the remaining companies have not published ESG reports separately, it does not mean that they have not disclosed ESG information. According to the statistical analysis of the annual reports of relevant companies, the vast majority of companies that do not publish separate ESG reports have elaborated on environmental and social responsibility and corporate governance related information in their annual reports.
According to the report, in the past three years, the proportion of ESG reports (including CSR reports and sustainability reports) released by listed building materials companies has continued to increase. As of July 2023, among the 125 listed companies in the building materials industry, 58 have separately released their 2022 ESG reports, an increase of 7 from 2022, a year-on-year increase of 13.7%, and an increase of 16 from 2021, an increase of 38.1%.
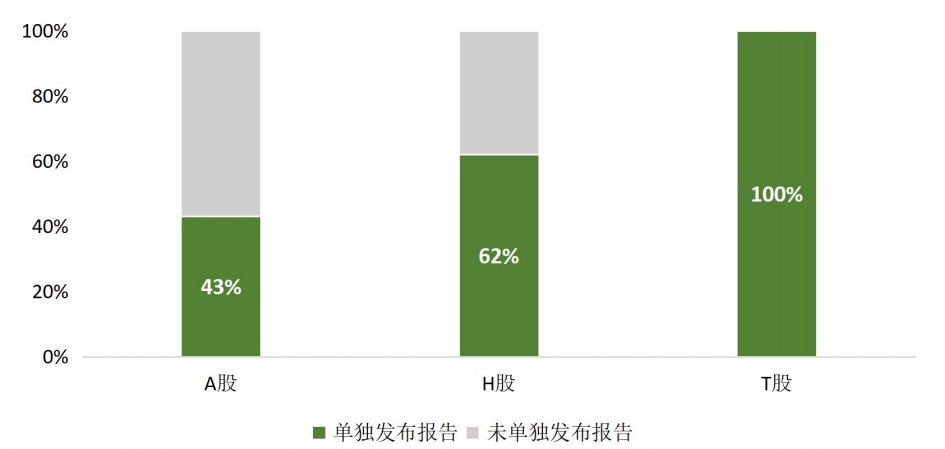
Based on the statistical results of China Construction Certification and MioTech, comparing the ESG reports disclosed separately by A-shares and H-shares in the past two years (including A+H-share companies listed at the same time), the average reporting rate of A-share companies is more than 31%, and the proportion of building materials companies is 43%. The average reporting rate of H-shares is more than 51%, and the proportion of building materials companies reporting separately is 62%, and the separate reporting rate of the building materials industry is generally higher than the average.
In addition, compared with non-state-owned enterprises, state-owned enterprises and central enterprises in the building materials industry are more active in releasing ESG reports. According to statistics, 22 of the 125 listed building materials companies are Chinese state-owned enterprises, of which 12 have released ESG reports separately (including 1 central enterprise), that is, the proportion of ESG reports published by the sample Chinese state-owned enterprises is 55%. Among the remaining 103 non-state-owned listed building materials companies, 46 have released ESG reports separately, accounting for 45%.
From the perspective of the industry as a whole, the quality of ESG information disclosure of cement, concrete and other building structural materials enterprises is relatively high. According to statistics, the main products of listed building materials companies involve cement, ready-mixed concrete and cement products, glass, ceramics and other 25 categories, according to the main business, production technology and application scenarios and other principles, the report will be divided into five categories: building structure materials, building envelope materials, decoration materials, building materials equipment and facilities, and comprehensive building materials.
Among them, the proportion of ESG reports issued by enterprises mainly engaged in building structural materials and decoration materials is higher than the industry average, and the proportion of ESG reports published by enterprises mainly engaged in building envelope materials and building materials, equipment and facilities is lower than the industry average.
The ESG information disclosure of building materials companies is becoming more and more standardized
ESG reports often refer to climate and sustainability-related standards
According to the report, the ESG information disclosure of building materials companies is becoming more and more standardized, and the quality of the report is improving year by year.
In recent years, some leading domestic companies have begun to gradually introduce international mainstream disclosure frameworks such as GRI (Sustainability Reporting Standards) and TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures Recommendations), and have responded to the concerns of relevant rating agencies, which are to a certain extent comparable to foreign companies in the same industry. At the same time, some leading companies in the building materials industry have gradually established a well-planned ESG governance system and put it into concrete action.
The reporter of this newspaper noticed that among the 125 companies studied in the report, many companies used GRI as the primary basis. For example, China Resources Cement Holdings Co., Ltd., Asia Cement Corporation (China) Holding Co., Ltd., Zhuyou Intelligent Manufacturing Technology Group Co., Ltd., Zhuyou Intelligent Manufacturing Technology Group Co., Ltd., etc.
It is reported that GRI is currently the most comprehensive and widely used ESG information disclosure standard. Based on this, the report also investigated the identification of material issues of 57 listed building materials companies that have published ESG reports in 2022 and found that 53.4% of the 57 companies identified and disclosed environmental compliance, 69.0% of emissions-related disclosures, 65.5% of energy disclosures, 69.0% of waste disclosures, and 51.7% of water resources and sewage-related disclosures.
In addition, the study found that there are large differences in the environmental material issues in the ESG reports of listed building materials companies, which the researchers of the report said are mainly due to the different types of main business and regional distribution of enterprises.
From the analysis of the main business type of the enterprise, cement and other building structure materials manufacturers attach great importance to environmental emissions and pollutant management, and most of the sample cement enterprises will reduce greenhouse gas emissions, waste emissions and pollutant management as high substantive issues, which is also determined by the "two highs" (i.e., high energy consumption and high emissions) characteristics of cement enterprises; Due to the relatively low carbon emissions of building materials, equipment and facilities, enterprises generally pay more attention to product-related waste management and other issues, and greenhouse gas emissions and climate change are rarely included in high-materiality issues.
From the analysis of the regional distribution of enterprises, the resource endowment and ecological environment conditions in different regions affect the identification of issues by building materials manufacturers to a certain extent. For example, Tianshan Cement in Xinjiang has listed water resource management as a "very important" issue, while in tropical and subtropical regions such as Yunnan and Taiwan, due to the diversity of ecosystems and species, local companies often include biodiversity as a "very important" issue.
It is worth noting that building materials companies in different formats and regions generally believe that environmental compliance is a very important substantive issue.
The industry's identification of key issues such as climate change needs to be strengthened
There is still a gap between domestic enterprises and foreign enterprises in terms of the quality of disclosure and the degree of responsiveness
According to the report, 93.8% of building materials companies on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange responded to climate-related disclosure requirements, 93% disclosed Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, and 93.4% disclosed environmental targets.
However, the report selected 57 sample companies that released their 2022 ESG reports and found that less than 70% of these companies disclosed greenhouse gas emissions, and only 29.3% of them considered the TCFD "governance-strategy-risk management-indicators and targets" framework and disclosed relevant climate change content, and the identification of key issues such as climate change in the building materials industry needs to be strengthened. This can also be seen in the ESG performance evaluation of building materials companies.
The report selects the performance evaluation system of five rating agencies: MSCI (MSCI), CSA (S&P Global Corporate Sustainability Assessment), FTSE Russell, MioTech (hereinafter referred to as MioTech), and the International Institute of Green Finance of the Central University of Finance and Economics (hereinafter referred to as the Green Finance Institute), and analyzes the performance evaluation results of 125 building materials companies, and finds that greenhouse gas emissions are the highest concern of the five rating agencies in the environmental field.
In recent years, with the acceleration of the domestic "dual carbon" process, the cement industry has greatly improved the deployment of carbon emission reduction technology and performance improvement. However, in terms of rating performance, foreign companies are generally higher than domestic ones.
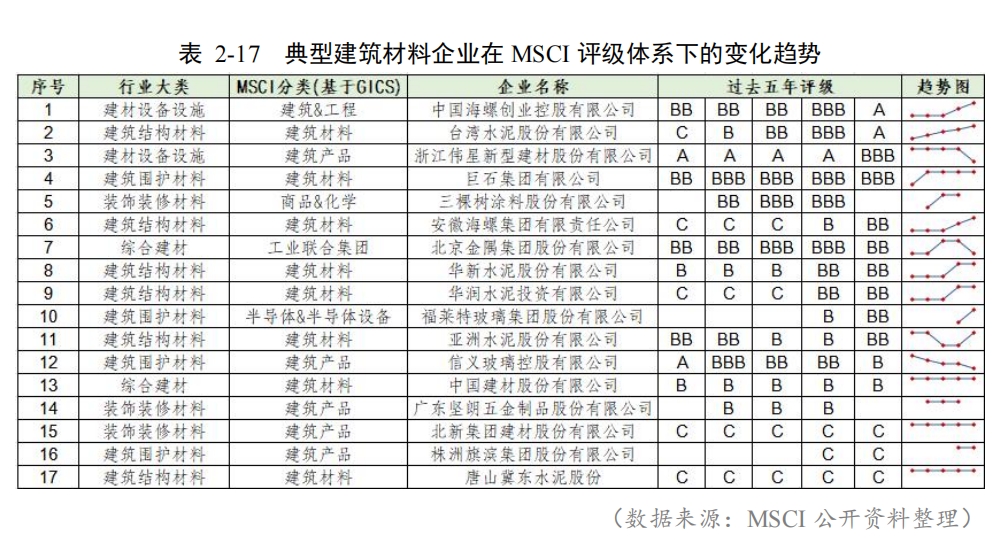
For example, there are 24 Chinese building materials companies included in the MSCI rating, and the carbon emission scores of enterprises in these industries are generally relatively low under the environmental theme, and the scores of toxic emissions and waste are high.
However, analysts related to the report said that the difference in the scores of domestic and foreign enterprises is more caused by the different disclosure methods followed by domestic and foreign enterprises and the requirements for the quality of disclosure.
It is reported that the disclosure of greenhouse gas emission information by foreign enterprises is basically based on TCFD (in June 2023, the ISSB newly released the "IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures", which integrates the TCFD framework) as the framework, and domestic enterprises have also begun to gradually standardize the disclosure of carbon emission information in recent years, such as Conch Group introduced the TCFD framework for the first time in 2021 to identify and assess climate change risk issues. However, on the whole, there is still a gap between domestic enterprises and foreign companies in terms of the quality of disclosure and the degree of responsiveness.
According to the research and analysis of the report, the information disclosed by domestic enterprises at the strategic and risk management level is relatively weak, and they are relatively conservative in the process of setting greenhouse gas emission targets.
Disclosure of sustainable development information by listed companies is a trend and requirement in the future. The Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges have also strengthened the disclosure requirements related to carbon emissions in the consultation on the Guidelines. That is, in addition to disclosing the content related to climate change governance and strategy, listed companies should also further disclose matters such as climate adaptation, transformation plans, total greenhouse gas emissions, emission reduction measures, and carbon emissions-related opportunities.







