11 departments issued the "Guidelines for the Construction of Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality Standard System"
On April 21, 11 departments, including the National Development and Reform Commission, the National Energy Administration, the National Standards Commission, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the Ministry of Natural Resources, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, the Ministry of Transport, the People's Bank of China, the China Meteorological Administration, and the National Forestry and Grassland Administration, jointly issued the Guidelines for the Construction of Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality Standard System (hereinafter referred to as the "Guidelines").
These guidelines are formulated so as to implement the major strategic decisions of the Party Central Committee and the State Council on carbon peaking and carbon neutrality, thoroughly implement the "National Standardization Development Outline", and accelerate the construction of a carbon peaking and carbon neutrality standard system with a reasonable structure, clear hierarchy, and adaptation to high-quality economic and social development in accordance with the relevant requirements of the "Implementation Plan for Establishing and Improving the Standard Measurement System for Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality".
1. General requirements
(1) Guiding ideology
Guided by Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, fully implement the spirit of the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, deeply practice Xi Jinping Thought on Ecological Civilization, base ourselves on the new stage of development, completely, accurately and comprehensively implement the new development concept, accelerate the construction of a new development pattern, adhere to the system concept, highlight the top-level design of standards, strengthen the effective supply of standards, pay attention to the benefits of standard implementation, coordinate the promotion of domestic and international, continue to improve the standard system, and strive to contribute to the realization of the goal of carbon peak and carbon neutrality.
(2) Basic principles
Stick to the system layout. Strengthen top-level design, optimize the dual structure of standards promulgated by the government and standards independently formulated by the market, strengthen cross-industry and cross-field standard coordination, improve the applicability and effectiveness of standards, and realize the convergence of various standards at all levels.
Stick to the key points. Accelerate the improvement of basic common standards. Focus on key areas and industries, and strengthen the formulation and revision of energy conservation and carbon reduction standards. Transform technological innovation achievements for carbon peaking and carbon neutrality into standards in a timely manner, and promote green development with scientific and technological innovation.
Persist in steady progress. Anchoring the short-term goal of carbon peak and carbon neutrality and long-term development needs, accelerating the updating and upgrading of standards, solidly promoting the development of standards, adhering to the combination of systematic promotion and emergency use, and implementing them in an orderly and steady manner on an annual and step-by-step basis.
Adhere to openness and integration. Solidly promote international exchanges and cooperation in standardization, actively participate in the formulation of international standards and rules, strengthen the overall planning of international standardization work, increase the promotion of Chinese standards abroad, and promote domestic and international coordination.
(3) Main objectives
Focusing on basic general standards, as well as the development needs of carbon emission reduction, carbon removal, and carbon market, a standard system for carbon peak and carbon neutrality has been basically established. By 2025, no less than 1,000 national standards and industry standards (including foreign language versions) will be formulated and revised, the degree of consistency with international standards will be significantly improved, the carbon accounting verification of major industries will achieve full coverage of the standards, and the energy consumption and energy efficiency standard indicators of key industries and products will be steadily improved. Substantive participation in no less than 30 green and low-carbon related international standards, and the level of green and low-carbon international standardization has been significantly improved.
Second, the standard system framework
The carbon peak and carbon neutrality standard system includes four first-level subsystems, including the basic general standard subsystem, the carbon emission reduction standard subsystem, the carbon removal standard subsystem and the market-oriented mechanism standard subsystem, and is further subdivided into 15 second-level subsystems and 63 third-level subsystems. The system covers key industries and fields such as energy, industry, transportation, urban and rural construction, water conservancy, agriculture and rural areas, forestry and grassland, finance, public institutions, and residents' lives, and meets the application of various scenarios such as regions, industries, parks, and organizations. This standard system is dynamically adjusted according to the needs of development.
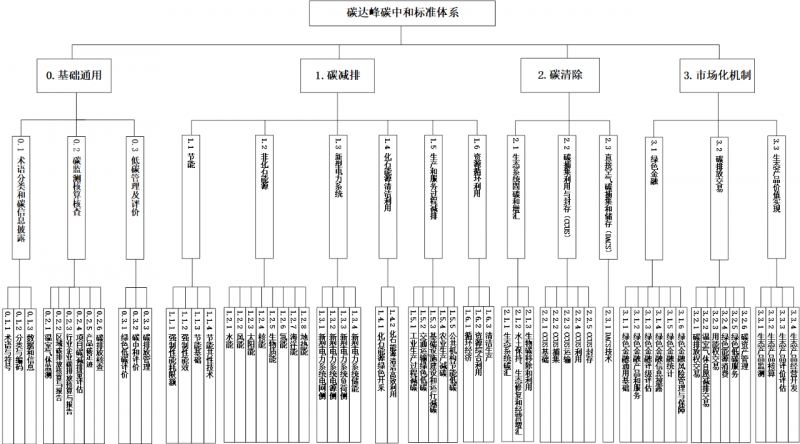
Third, the key construction content of the standard
(1) Basic general standard subsystem
1. Terminology, classification, and carbon disclosure standards
Focus on formulating and revising terms and definitions related to greenhouse gases and climate change management, technical specifications for carbon emission data classification and coding, carbon emission information collection methods and requirements, carbon information disclosure and other standards.
2. Carbon monitoring, accounting, and verification standards and specifications
Focus on formulating and revising standards for carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gas monitoring methods, monitoring equipment, online monitoring systems and carbon control platform construction, and relevant standards for long-term dynamic observation, monitoring, evaluation and forecasting of the physical and chemical characteristics of atmospheric components. Formulate and revise regional carbon emission accounting and reporting standards for regions, parks and other regions. Accelerate the formulation and revision of carbon emission accounting and reporting standards for enterprises in key industries such as energy, metallurgy, building materials, chemicals, nonferrous metals, textiles, machinery, information and communication, transportation, and livestock and poultry breeding, as well as standards and specifications related to data quality. Improve the assessment standards for carbon emission reductions of typical projects such as energy efficiency improvement, renewable energy utilization, raw fuel substitution, residual energy utilization, biomarine forest and grass soil carbon sequestration, and livestock and poultry breeding. Develop general standards such as product carbon footprint quantification and type rules, and explore the formulation of carbon emission accounting and carbon footprint standards for key products. Formulate and revise basic common standards such as carbon emission verification procedures, personnel and institutions.
3. Low-carbon management and evaluation standards
Focus on formulating and revising green and low-carbon assessment and environmental impact assessment standards for cities, facilities, enterprises, supply chains, parks, technologies, etc., green product evaluation standards, green and low-carbon industry statistical accounting standards, carbon neutrality evaluation general principles standards, and general standards for carbon peak and carbon neutrality related planning and design, management systems and implementation evaluation in different application scenarios.
(2) Carbon emission reduction standard subsystem
1. Energy saving standards
Accelerate the formulation and revision of mandatory energy consumption quota standards for key industries such as thermal power, iron and steel, building materials, chemicals, nonferrous metals, coal, mining, light industry, machinery, and transportation, and promote the coordination of energy consumption quota indicators and carbon emission intensity indicators. Adhere to the synergy between pollution reduction and carbon reduction, and the combination of source and end, and give full play to the role of standard reversal, optimization, adjustment and promotion. In line with the international advanced level, we will improve the mandatory energy efficiency standards for key products and equipment such as household appliances, heating equipment for rural residents, refrigeration and cold chain logistics equipment, industrial equipment, lighting products, data centers, new and renewable energy equipment, and machinery manufacturing equipment. Accelerate the improvement of energy consumption calculation, energy efficiency testing, energy conservation assessment, energy conservation acceptance, energy audit and other standards supporting mandatory energy-saving standards.
Accelerate the formulation of basic standards such as energy-saving design and planning, energy balance calculation, energy management system, energy performance evaluation, economic operation, rational energy use, energy-saving diagnosis, energy-saving services, and green energy-saving organization evaluation. Improve energy-saving common technical standards such as energy efficiency benchmarking, energy-saving technology evaluation, system energy conservation, energy recovery, residual energy utilization, energy system optimization, high-efficiency energy-saving equipment, energy-saving monitoring, energy-saving measurement and verification, energy metering, digital empowerment technology, district energy system, distributed energy system, and energy management and control center.
2. Non-fossil energy standards
In the field of hydropower generation, it is important to formulate and revise standards for the expansion and efficiency of hydropower units, stable operation under wide loads, evaluation of operating status and life extension, as well as technical standards for green development of small hydropower, ecological flow, safety appraisal and other green development.
In the field of wind power generation, it is important to formulate and revise standards for wind energy resource monitoring, evaluation, wind forecasting and forecasting, standards for wind turbines and key components, standards for fire protection systems, standards for materials used in wind power towers, construction standards for offshore wind power generation projects and grid-connected standards, and standards for calculation of wind power system stability.
In the field of photovoltaic power generation, it focuses on formulating and revising technical standards for solar energy resource monitoring, evaluation and radiation forecasting and prediction, technical requirements, flame retardant and fire resistance performance requirements, testing methods and green and low-carbon standards for key products of high-efficiency photovoltaic cells, modules and key materials, electrical components and support structures, and standards for repair, transformation, life extension and recycling of major products and equipment such as photovoltaic modules, brackets and inverters.
In the field of solar thermal utilization, it is important to formulate and revise standards for solar thermal power generation equipment, as well as standards for the prediction and prediction of solar normal direct radiation. Improve the product standards and testing and evaluation standards for key components of solar thermal collection, solar heating and cooling systems, and solar multi-energy complementary systems.
In the field of nuclear power generation, the focus is on formulating and revising technical standards for nuclear power, risk management standards for nuclear power plants, standards for evaluating the effectiveness of maintenance, and evaluation standards for nuclear power plant sites.
In the field of biomass energy, it is important to formulate and revise standards for raw material quality control, key technologies and equipment, and product quality grading in domestic waste incineration power generation, agricultural and forestry biomass thermal power, biomass clean heating, bio-natural gas (biogas), biomass pyrolysis and gasification, biomass liquid fuel and biomass pellet fuel.
In the field of hydrogen energy, we will focus on improving the technical standards of the whole industry chain, accelerate the formulation and revision of basic general standards such as hydrogen fuel quality and hydrogen energy testing, hydrogen and hydrogen system safety and risk assessment standards, hydrogen sealing, hydrogen materials, hydrogen leak detection and explosion prevention and explosion suppression, hydrogen safety venting standards, hydrogen supply mother stations, oil, gas, hydrogen and electricity integrated energy station safety standards and other hydrogen energy safety standards, water electrolysis hydrogen production systems and their key components, refinery hydrogen preparation and testing standards, hydrogen liquefaction equipment and liquid hydrogen storage containers, high-pressure gaseous hydrogen transportation, pure hydrogen/ Hydrogen storage and transportation standards such as hydrogen doping pipelines, hydrogen refueling station systems and their key technologies and equipment standards, fuel cell, metallurgy and other fields of hydrogen energy application technology standards.
In the field of marine energy and geothermal energy, it is important to formulate and revise standards for the testing, evaluation, deployment and operation of marine energy power generation equipment, as well as standards for geothermal power generation equipment.
3. New power system standards
In the field of power grid, it is important to formulate and revise technical standards for substation secondary systems, AC and DC hybrid microgrid operation and protection standards, new energy grid connection, distribution network and energy Internet and other technical standards.
In the field of power supply, we will focus on formulating and revising standards for distributed power operation control, power quality, and power forecasting.
In the load-side field, we will focus on formulating and revising standards for load forecasting, demand-side management, and virtual power plant construction, evaluation, and access in the power market.
In the field of energy storage, it is important to formulate and revise pumped storage standards, new energy storage standards such as electrochemistry, compressed air, flywheel, gravity, carbon dioxide, heat (cold), hydrogen (ammonia), superconductivity, etc., and safety management and emergency disposal standards for energy storage systems connected to the power grid and energy storage systems.
4. Standards for the clean use of fossil fuels
In the field of coal, it is important to formulate and revise standards for coal screening, geological environment investigation in subsidence areas, evaluation of ecological restoration effectiveness, intelligent coal sample preparation, laboratory system performance, and component type determination.
In the petroleum sector, it will focus on formulating and revising technical standards for low-carbon oil exploitation and refining, as well as fuel standards for low-emission, high-calorific value and high-thermal efficiency.
In the field of natural gas, it is important to formulate and revise LNG quality, flow measurement, sampling guidelines, composition analysis and determination, tail gas treatment and evaluation, pipeline transportation requirements and shale gas technical standards.
5. Emission reduction standards for production and service processes
In the field of carbon reduction in industrial production processes, key technical standards and supporting standard samples for low-carbon carbon sequestration technology, low-carbon technology and equipment, non-carbon dioxide greenhouse gas emission reduction technology, raw fuel substitution technology, low-carbon detection technology, low-carbon measurement and analysis technology, green manufacturing, water conservation and other industries in steel, petrochemical, chemical, non-ferrous metals, building materials, machinery, papermaking, textile, automobile, food processing and other industries will be revised.
In the field of green and low-carbon transportation, we will focus on formulating and revising energy efficiency standards for infrastructure and equipment in the fields of railways, highways, water transportation, civil aviation, and postal services, as well as standards for green equipment and facilities for logistics, efficient transportation organization, green travel, low-carbon and diversified power application of transportation vehicles, green transportation station facilities, transportation energy integration, and industry pollution and carbon reduction. Accelerate the improvement of technical standards for energy storage trams, energy storage systems, power battery systems, and electric energy measurement in the field of rail transit. Improve the relevant standards for energy consumption limits and labels for road vehicles, energy consumption calculation tests and evaluation methods. Accelerate the improvement of standards related to safety requirements, performance requirements, test methods, remote service management, and safety technical inspection of electric vehicle drive systems, charging and swapping systems, and power battery systems. Accelerate the research and formulation of the next stage of emission standards for motor vehicles, and promote the synergy of motor vehicle pollution reduction and carbon reduction.
In the field of infrastructure construction and operation carbon reduction, it is important to formulate and revise standards for low-carbon construction of urban infrastructure, carbon reduction of urban housing, construction of low-carbon smart parks, low-carbon transformation of rural houses, green construction, resource utilization of sewage and garbage, desalination, standards for construction waste recycling equipment, air source heat pump equipment, etc., as well as standards for the construction, operation and maintenance, use metering, and recycling of information and communication infrastructure such as communication networks, data centers, and communication equipment rooms for energy-saving and low-carbon goals.
In the field of carbon reduction in agricultural production, it is important to formulate and revise technical standards for greenhouse gas emission reduction in the planting industry, as well as emission reduction standards for the production process of the livestock industry, such as animal intestinal methane emission reduction technology, livestock and poultry liquid manure emission reduction technology, and improve energy-saving and low-carbon standards for factory agriculture, large-scale farming, and agricultural machinery.
In the field of energy conservation and low-carbon in public institutions, it is important to formulate and revise the standards for energy and resource conservation and green transformation of typical public institutions such as organs, hospitals, and schools, as well as the evaluation standards for energy-saving institutions, green schools, green hospitals, and green venues, as well as the management standards for low-carbon construction and low-carbon economic operation of public institutions.
6. Resource Recycling Standards
Focus on formulating and revising standards for circular economy management and performance evaluation. Promote the formulation and revision of the general principles and standards for the evaluation of cleaner production, the standards for the comprehensive utilization of rare earths and vanadium titanomagnetite, and the standards for the comprehensive utilization of bulk solid wastes such as phosphogypsum, red mud, and smelting waste residue. Formulate and revise standards for the recycling of renewable resources such as scrap metal, waste textiles, waste plastics, and waste power batteries. Accelerate the improvement of water reuse standards. Formulate and revise remanufacturing standards for auto parts, internal combustion engines, mechanical tools, etc. Formulate and revise the standards for resource recycling in the forestry and grass industry.
(3) Carbon removal standard subsystem
1. Ecosystem carbon sequestration and sink enhancement criteria
Focus on formulating and revising general standards related to terminology, classification, boundaries, monitoring, and measurement of carbon sinks in terrestrial, lake and marine ecosystems and carbon sinks of wood forest products, as well as standards and technical standards for the protection of forests, grasslands, artificial grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, deserts, mines, karst, oceans, soils, permafrost and other resources, ecological restoration, protection of water and soil resources and comprehensive management of soil erosion, carbon sequestration and sink, and management of carbon sequestration and sink, and technical standards for the protection and management of forest and grass resources, and standards for forest and bamboo enhancement management, wood and bamboo substitution, and forestry biomass products, as well as standards for biological carbon removal and utilization, selection and breeding of high-efficiency carbon sequestration tree species, grass seeds, and algae species. Research and formulate relevant standards for meteorological support for ecological restoration.
2. Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage Standards
Focus on formulating and revising basic standards such as terminology and assessment related to carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS), standards for carbon emission capture from combustion, and improvement of standards for carbon dioxide pipeline transportation. Promote the formulation of carbon utilization standards such as carbon dioxide flooding (EOR), chemical utilization, biological utilization, and fuel utilization, as well as carbon storage standards such as onshore storage and offshore storage.
3. Direct Air Carbon Capture and Storage Standards
Focus on formulating and revising standards for direct air carbon capture and storage (DACS) application conditions, technical requirements, and implementation effect evaluation.
(4) Market-oriented mechanism standard subsystem
1. Green Finance Standards
Focus on formulating and revising basic general standards such as green finance terminology, carbon accounting for financial institutions, carbon account management of banks, enterprises and individuals, climate investment and financing and transition finance taxonomy, and green financial product and service standards for green loans, green bonds, green insurance, and carbon financial derivatives trading. Promote the formulation and revision of green finance evaluation and evaluation standards such as green bond credit ratings. Improve standards for information disclosure of financial institutions and financial business environment.
2. Standards and specifications related to carbon emission trading
Formulate and revise standards and specifications for the allocation, adjustment, settlement, and offsetting of carbon emission allowances. Improve the implementation specifications of carbon emission trading, as well as the relevant standards and specifications for carbon emission trading institutions and personnel. Promote the formulation and revision of standards and specifications such as emission reduction accounting methods for voluntary emission reduction projects in key areas. Improve green energy consumption standards such as statistical accounting, monitoring, and evaluation of renewable energy consumption, as well as green electricity trading。 Improve standards for green and low-carbon technology assessment services, contract energy management, and carbon asset management.
3. Ecological product value realization standards
Focus on formulating and revising standards for the confirmation of natural resource rights, the investigation of ecological product information, and the dynamic monitoring of ecological products. Improve evaluation standards for ecological products, ecological assets, ecosystem service functions, and gross ecosystem production. Improve standards for comprehensive ecological improvement, mine pit restoration, water ecological management, comprehensive soil erosion control, comprehensive land improvement, as well as standards for ecological agriculture and ecological product quality traceability. Promote the formulation and revision of technical standards for the appraisal and assessment of ecological and environmental damage, as well as standards for the evaluation of the performance of ecological product value realization.
Fourth, the focus of international standardization work
(1) Form a joint force for international standardization work
Led by the State Administration for Market Regulation (Standards Committee), the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, with the participation of foreign affairs, commerce, international cooperation, science and technology, natural resources, housing and urban-rural construction, transportation, agriculture and rural affairs, energy, forestry and grassland, and other departments, the International Standardization Coordination and Promotion Working Group for Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality has been established to actively and steadily promote international standardization. Give full play to China's technological advantages in carbon capture and storage, new power systems, new energy and other fields, set up a number of international standard innovation teams, gather the strength of scientific and technological researchers and standardization experts, and simultaneously deploy scientific research and international standard formulation.
(2) Strengthen international exchanges and cooperation
Strengthen cooperation and docking with the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), International Standards Organizations (ISO, IEC, ITU) and other institutions, focus on green energy transformation, industry, urban and rural construction, transportation, new infrastructure, carbon sinks, green and low-carbon technology development, circular economy and other key points, and track the latest international developments in the field of carbon peak and carbon neutrality. In-depth study of relevant standardization policies and technical trade measures in the European Union, the United States and other regions and countries. Strengthen standardization exchanges and cooperation with key regions and countries, and promote the construction of a green "Belt and Road". Increase the publicity and use of China's carbon peak and carbon neutrality standards in standardized foreign aid training or overseas engineering projects. Promote dialogue on energy-saving and low-carbon standardization under the framework of BRICS and APEC, and develop mutually beneficial and win-win standardization partnerships.
(3) Actively participate in the formulation of international standards
Focus on promoting the proposal of international standards such as greenhouse gas emission monitoring and accounting, forest and grass carbon sequestration and sink enhancement, clean and low-carbon utilization of traditional energy in the energy field, smart grid and energy storage, new power systems, clean energy, green finance, information and communication fields and digital empowerment, and promote the development of standards. Actively strive to establish regional energy systems, medical refrigeration equipment, ecological carbon sinks and other technical institutions in the international standards organization. Deeply participate in the work of international standards organizations in addressing climate change, and recommend Chinese experts to participate in strategic research and coordination governance bodies such as the Climate Change Coordination Committee (CCCC), the Environmental and Social Governance (ESG) Coordination Committee, and the Energy Structure Special Committee (CEET) of the Independent Advisory Committee of the United Nations Secretary-General. Actively cooperate with relevant countries to formulate and release policy white papers such as "Multi-energy Intelligent Coupled Energy System" and "Multi-source Solid Waste Energy".
(4) Promote the docking of domestic and international standards
Carry out comparative analysis of domestic and international standards for carbon peak and carbon neutrality, and focus on promoting the transformation of applicable international standards in the fields of greenhouse gas management, carbon footprint, carbon capture, utilization and storage, clean energy, and energy conservation into China's standards, so as to achieve "full extraction" in a timely manner. We will systematically promote the formulation, publicity and promotion of foreign language versions of national standards, industry standards, and local standards for carbon peak and carbon neutrality, and expand the overseas application of China's standards through various channels such as product and service trade, international cooperation, and overseas projects.
5. Organization and implementation
(1) Persist in overall planning and coordination
Strengthen the overall deployment and systematic promotion of the construction of the carbon peak and carbon neutrality standard system, give full play to the overall planning and technical coordination role of the national carbon peak and carbon neutrality standardization group, strengthen the guidance for the construction of various standard subsystems, and strengthen the coordination of national standards and industry standards. Establish and improve the liaison mechanism of the National Standardization Technical Committee, and jointly promote the development of cross-industry and cross-field standards through the establishment of joint working groups, joint formulation, and joint centralization. Give full play to the role of the industry's relevant standardization coordination and promotion organizations, and coordinate and promote the standardization of carbon peak and carbon neutrality in the industry.
(2) Strengthen the implementation of tasks
All industries and fields should accelerate the formulation and revision of relevant national standards and industry standards in accordance with the content of the construction of the carbon peak and carbon neutrality standard system, and do a good job in the effective connection between professional field standards and basic general standards, newly formulated standards and issued standards. All localities and social organizations have strengthened cooperation with standardization technical organizations, and promoted the formulation and revision of local standards and group standards for carbon peaking and carbon neutrality in accordance with local conditions and in parallel at multiple points in accordance with the law. We will continue to increase investment to support the research, formulation, implementation, and international exchange of key standards.
(3) Strengthen publicity and implementation
Widely carry out the publicity work of carbon peak and carbon neutrality standardization, make full use of radio, television, newspapers, the Internet and other media to popularize the knowledge of carbon peak and carbon neutrality standardization, and improve the public's awareness of green and low-carbon standardization. Organize and carry out the evaluation of the construction of the carbon peak and carbon neutrality standard system in a timely manner, summarize typical cases of carbon peak and carbon neutrality standardization in a timely manner, and promote advanced experience and practices.







