With the release of the CATI index, the climate information disclosure of A-share listed companies needs to be strengthened urgently
At the press conference of the environmental responsibility information disclosure evaluation report of China's listed companies held recently, the Institute of Public and Environmental Affairs (IPE) of social organizations released the 2023 CATI index evaluation results of climate action of listed companies.
The 2023 Corporate Climate Action CATI Index covers a total of 880 A-share and H-share listed companies, including Luxshare Precision (002475), Lenovo Group (00992), Pengding Holdings (002938), and LONGi Green Energy (601012), Baosteel (600019) and Anta Sports (02020) were rated BBB, and USI (601231), Fortune Federation of Industry (601138), Companies such as Sinopec (600028) are also leading the way in climate action.
For investors' understanding, the CATI index evaluation results are expressed in terms of AAA, AA, A, BBB, BB, B, CCC, CC, and C. Compared with the results of the CATI evaluation of the 497 companies included in the evaluation for two consecutive years, the climate action of listed companies has made good progress: the number of A-rated enterprises has increased to 4, the proportion of B-rated companies and above has increased from 9% to 17%, the proportion of CCC and CC-rated enterprises has increased by 5% and 7% respectively, and the relatively backward C-rated enterprises have decreased from 65% to 45%, and more companies have accelerated the process of reducing emissions. Among the total 880 companies evaluated in 2023, 12% of the B-level and above companies have increased, but 56% of the C-level companies with relatively backward performance are still behind.
H-share listed companies outperformed A-shares
This evaluation involves A-share and H-share listed companies, among which H-share (including AH-share) listed companies outperformed A-share listed companies. IPE analysis believes that the disclosure requirements for climate information of listed companies are more clear than those of A-shares, and following the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) issued the International Financial Reporting Sustainability Disclosure Standard No. 2 – Climate-related Disclosures, the Hong Kong Stock Exchange has made it clear that it intends to implement mandatory disclosure. In this regard, Ma Jun, director of IPE, suggested that the Shanghai Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exchange should benchmark the disclosure standards of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange as soon as possible, and at the same time refer to the ISSB climate-related disclosure guidelines, improve the relevant disclosure rules of A-shares, guide the climate information disclosure of listed companies to be in line with international standards, and formulate climate information disclosure frameworks and standards suitable for Chinese enterprises, so as to promote the effective disclosure of corporate climate-related data and management measures, and empower enterprises to start efficient carbon management through the application of the latest digital technology.
On February 8, under the unified deployment of the China Securities Regulatory Commission, the Shanghai Stock Exchange, Shenzhen Stock Exchange and Beijing Stock Exchange respectively solicited public opinions on the "Sustainability Reporting Guidelines" (hereinafter referred to as the "Guidelines") to standardize the sustainability disclosure framework, including climate information disclosure requirements. IPE analyzed the performance of 161 companies expected to be included in the scope of disclosure in the CATI index evaluation according to the standards of disclosure entities in the draft of the Guidelines, of which 3 were rated A, about 26% of the companies entered BBB to B grades, and about 32% of the C-rated companies with relatively backward performance were rated. The overall level of climate disclosure of listed companies included in the disclosure scope is higher than the average, but in the face of the new disclosure regulations, most companies still need to strengthen relevant capacity building.
Listed companies of central enterprises have made significant progress
The average score of the listed companies of central enterprises involved in this evaluation in 2023 has increased significantly by nearly 3 points compared with 2022, among them, the performance of leading companies such as Baosteel (600019), Sinopec (600028), PetroChina (601857), Huadian International (600027), and Huaneng International (600011) has improved, TISCO Stainless (000825), Shenzhen Tianma A (000050), Anshan Iron and Steel (000898), China Resources Beer (00291) and Yituo (601038) have made great progress.
According to this evaluation, in terms of governance and management, more than 90% of the evaluated companies have issued climate declarations and formulated climate policies. In terms of measurement and disclosure, nearly 70% of companies have calculated and publicly disclosed carbon data, with a total of 37 disclosures. 600 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent.
In terms of target setting, 23% of the evaluated companies have set and disclosed Scope 1&2 emission reduction targets, 30 companies including LONGi Green Energy (601012), ZTE (000063) and SF Holding (002352) have released Scope 3 emission reduction targets, and 26 companies including Lenovo Group (00992), Pengding Holdings (002938) and Baosteel (600019) have further set carbon neutrality targets including Scope 3. A company's direct and indirect GHG emissions are divided into 3 "scopes", with Scope 1 emissions being direct GHG emissions from sources owned or controlled by the company. Scope 2 emissions are indirect greenhouse gas emissions from a company's use of purchased electricity, heating/cooling, or steam. Scope 3 emissions are all other indirect greenhouse gas emissions in a company's value chain.
According to this evaluation, about ninety percent of listed companies have carried out emission reduction actions of different scales. Among them, 71% of the participating companies have reduced greenhouse gas emissions from their own operations (Scope 1 & 2) through renewable energy utilization, energy efficiency improvement, process adjustment, and investment in carbon sequestration projects. In response to Scope 3 emissions, Luxshare Precision, Lenovo Group, Pengding Holdings, Anta Sports, Fortune Alliance, Lens Technology and Goertek have encouraged their suppliers to disclose carbon data and emission reduction targets through third-party platforms, so as to improve suppliers' independent carbon management capabilities and track the progress of supply chain emission reduction through measured data. Eight percent of the participating companies also used methods such as product life cycle assessment to identify emission hotspots and carry out pilot emission reduction projects with core suppliers.
The listed companies evaluated in this issue involve 36 industries, including energy, steel, nonferrous metals, petrochemicals and other energy-consuming industries, as well as consumer goods industries such as IT, textiles, e-commerce, food and beverage, as well as emerging industries such as photovoltaic equipment, batteries and new energy vehicles. Judging from the evaluation results of sub-industries, the progress of steel and other industries is quite outstanding, with a year-on-year increase of 54%. Ding Shanshan, director of IPE green supply chain, believes that this reflects the positive efforts made by Baosteel and other enterprises and platforms such as the China Iron and Steel Association to respond to the requirements of the dual carbon policy and the market demand for low-carbon steel.
Most companies have yet to translate policies into action
While overall progress has been made, only 12% of companies rated B or above in this evaluation suggest that the overall climate performance of China's listed companies needs to be improved. According to IPE analysis, ninety percent of the participating companies have formulated and released climate policies, but most of them have yet to translate them into effective climate actions, and enterprises need to improve their own governance and management mechanisms based on the dual carbon goals, benchmark global temperature control goals and nationally determined contributions (NDCs), scientifically set corporate carbon neutrality targets, and publicly disclose annual progress.
According to the United Nations Environment Programme's 2023 Emissions Gap Report, to meet the 2°C target set by the Paris Agreement, projected emissions must be reduced by 28% by 2030 to achieve 1. 5°C target to reduce emissions by 42%. Zhu Ziqi, head of CATI index evaluation of IPE listed companies, said that listed companies, as an important subject of carbon emissions, should be clearly aware of the expectations of all sectors of society and their own pressure to reduce emissions, and use the evaluation results of CATI index to benchmark international and domestic good practices and effectively improve climate action performance.
At the same time, the low-carbon transition of global enterprises needs a lot of support, and Zhu Ziqi hopes that this index evaluation report can provide effective information for the capital market, help investors understand the climate action performance of participating listed companies, identify the risk of climate "greenwashing", and help climate investment and financing.
On the other hand, investors also need to improve the climate information disclosure requirements of financing companies as soon as possible, and use professional tools to identify and quantify climate risks and track changes in greenhouse gas emissions of enterprises. In addition, financial institutions urgently need to formulate corresponding climate investment and financing plans based on the production processes and emission characteristics of different industries, and develop diversified financing mechanisms and tools to support enterprises to accelerate the green and low-carbon transformation.
As a data-based independent evaluation system, the CATI index can objectively reflect the progress of the participating companies' climate actions and the situation in the dual carbon action, and form a consensus on accelerating climate governance and implementing energy conservation and emission reduction measures. The CATI index can also provide a roadmap for enterprises to start climate action, and guide them to carry out greenhouse gas accounting, Starting with the creation of a greenhouse gas inventory, identify hot emission sources, set quantitative emission reduction targets and formulate targeted emission reduction plans, decompose emission reduction targets into major production links and value chains, carry out large-scale emission reductions according to the emission reduction pathways of their industries, track and disclose the progress of target completion, and drive and empower upstream and downstream partners to start climate action.
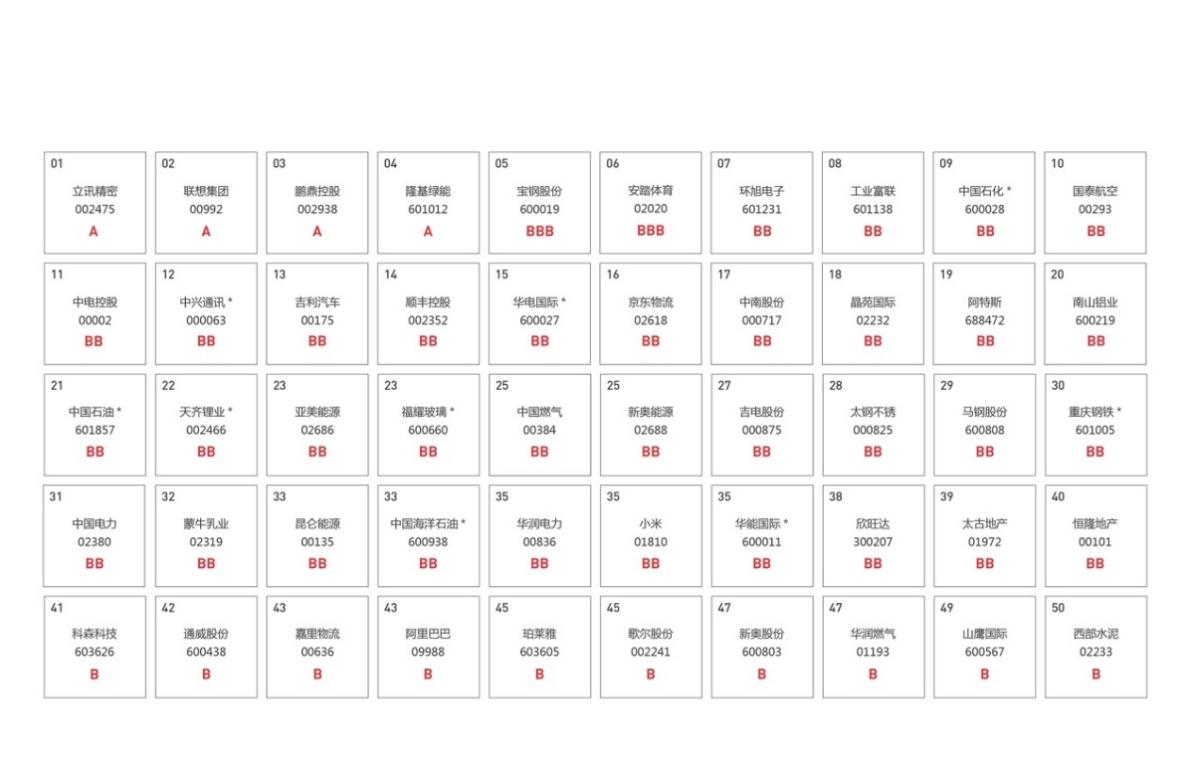
Figure 2023 Top 50 Listed Companies Corporate Climate Action CATI Index







